A prominent example of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is Amazon Web Services (AWS) Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2). It allows users to rent virtual servers & compute power on demand, enabling businesses to scale resources up or down based on their needs. This flexibility eliminates the need for physical hardware, reduces costs, & enhances operational efficiency. With AWS EC2, users can deploy applications quickly & manage them with ease, making it a preferred choice for companies seeking cloud infrastructure solutions.
What is an Example of IaaS? Understanding Infrastructure as a Service. Discover what IaaS means with our easy guide. Learn about Infrastructure as a Service & see real-world examples to simplify your understanding.

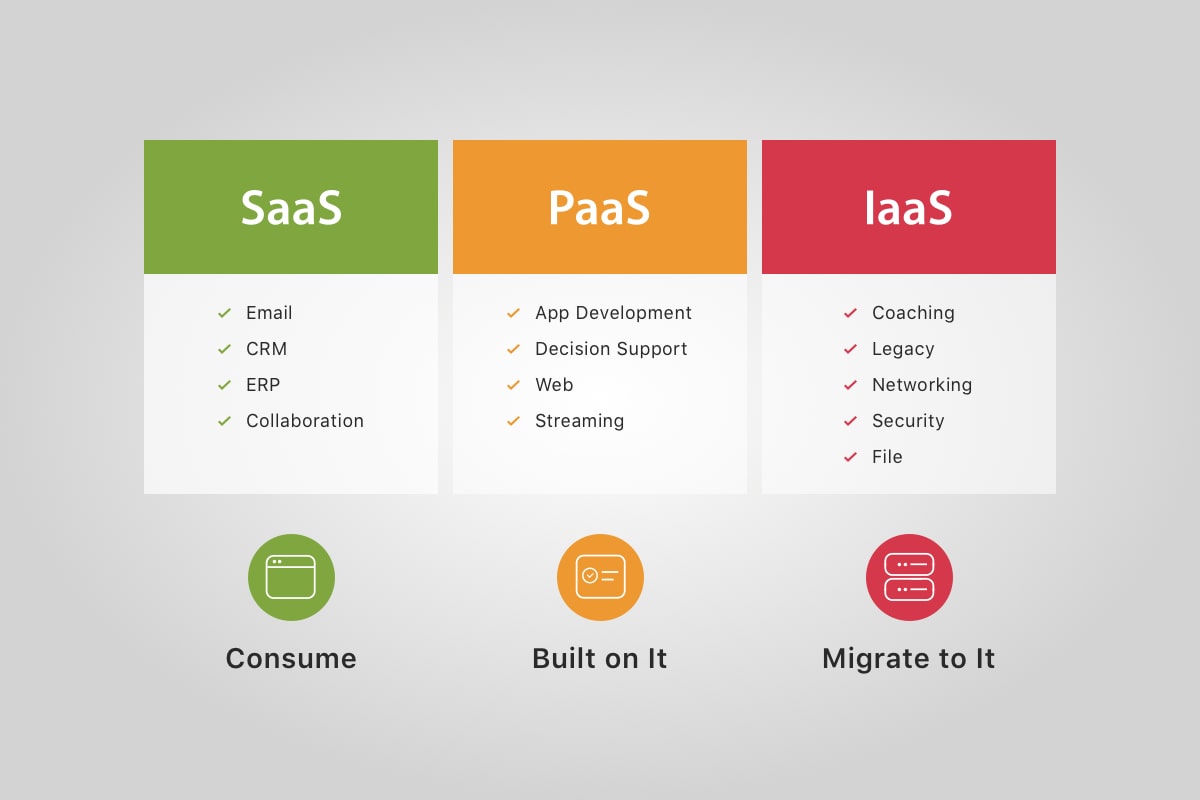
The main DIFFERENCES between IaaS, SaaS & PaaS explained…
What is an Example of IaaS? Understanding Infrastructure as a Service The main DIFFERENCES between IaaS, SaaS & PaaS explained… What is an Example of IaaS? Understanding Infrastructure as a Service
Understanding IaaS: A Comprehensive Look
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) represents a fundamental component within cloud computing. This service allows organizations access to virtualized computing resources over Internet. Rather than investing in physical hardware, companies can rent computing resources, like servers, storage, & networking. IaaS provides flexibility, scalability, & a cost-effective solution for managing IT infrastructure. By leveraging this service, businesses navigate operational challenges while ensuring uninterrupted access to necessary computing capabilities.
Key Characteristics of IaaS
Several distinctive features define IaaS offerings. One major characteristic involves on-demand availability. Organizations can provision computing resources as needed without significant delays. Another important factor relates to resource pooling. Multiple customers share infrastructure resources, which leads to enhanced utilization & reduced cost. And another thing, IaaS provides scalability, enabling businesses to adjust their resource consumption according to fluctuating demands. This flexibility proves essential, especially for companies experiencing rapid growth or those with variable workloads.
On top of that, IaaS supports automation which simplifies management processes. For instance, users can automate tasks like deployment, scaling, & monitoring. This automation saves time & reduces human error in operations. Security also becomes a priority; many IaaS providers implement various security measures, ensuring data protection & compliance. With these features, organizations can focus on innovation rather than infrastructure management, allowing more agility in their operations.
In my experience, utilizing an IaaS solution significantly transformed our approach to infrastructure management. Instead of facing downtime due to hardware failures, we could swiftly allocate additional resources whenever necessary. This model proved invaluable during peak usage times, ensuring seamless service delivery.
Major IaaS Providers
Several players dominate IaaS market, each offering unique features & advantages. Industry leaders ensure robust service offerings, drawing enterprises requiring reliable infrastructure support. By examining major IaaS providers, organizations can make informed decisions about which services best fit their needs.
Leading Providers
- AWS (Amazon Web Services)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform
- IBM Cloud
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
| Provider | Features | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|
| AWS | Wide range of services, global infrastructure | Pay-as-you-go |
| Microsoft Azure | Integration with Microsoft software | Per minute billing |
| Google Cloud | Data analytics capabilities | Pay-for-what-you-use |
Benefits of Using IaaS
Adopting IaaS brings numerous benefits, particularly for businesses aiming for efficiency & cost-effectiveness. One clear advantage lies in reduced capital expenditures since organizations avoid investing upfront in physical hardware. Instead, they pay only for resources consumed. This shift enables businesses to allocate finances toward innovation rather than maintenance.
And don’t forget, IaaS enhances flexibility. Organizations can quickly scale up or down based on current projects or workload demands. This agility fosters a more responsive business environment, allowing teams to seize market opportunities with confidence. And another thing, IaaS allows companies access to advanced technologies without needing in-house expertise, streamlining the adoption of cutting-edge solutions.
Security constitutes another key benefit of IaaS usage. Leading providers implement rigorous security measures, including encryption, firewalls, & compliance certifications. As a result, organizations experience peace of mind knowing that sensitive data receives robust protection from unauthorized access.
Types of IaaS Solutions
IaaS encompasses various solutions tailored to meet diverse organizational needs. Understanding these options enables companies to select services aligning with their specific objectives. Some key types include public IaaS, private IaaS, & hybrid IaaS solutions.
Public IaaS utilizes shared resources over Internet, allowing organizations access to scalable capabilities without significant investment. This model often suits startups or smaller businesses aiming to minimize costs & scale quickly. Private IaaS offers dedicated infrastructure for specific organizations, enhancing security & performance. This model best serves larger enterprises with stringent regulatory requirements or unique workload demands.
Hybrid IaaS solutions combine both public & private offerings, providing businesses with increased flexibility & control. Organizations can keep sensitive data secure within a private environment while utilizing public resources for less critical applications, thus optimizing costs & responsiveness.
Integrating IaaS with Existing Infrastructure
Organizations already possessing existing infrastructure can effectively integrate IaaS solutions into their operations. This integration allows companies to leverage current investments while simultaneously benefiting from cloud capabilities. One approach involves adopting a hybrid model where businesses utilize IaaS for specific projects or workloads while continuing to operate their on-premises systems.
Another valuable strategy includes deploying IaaS for disaster recovery. By establishing backup systems in the cloud, organizations ensure data continuity without significant investment in additional on-premises hardware. This method enhances resilience & safeguards critical operations against potential disruptions, ultimately leading to improved business continuity.
Conducting a thorough analysis of workloads also aids organizations in determining which applications or services may benefit most from IaaS implementation. Companies should consider factors such as performance requirements, security, & compliance when making decisions about cloud adoption.
Common Use Cases for IaaS
IaaS serves various industries & businesses, providing solutions for multiple use cases. Businesses often turn to IaaS for hosting applications & websites. By utilizing robust cloud infrastructure, organizations gain scalability & reliability necessary for user satisfaction.
And another thing, IaaS plays a crucial role in development & testing environments. Developers can quickly provision resources as required for software projects, expediting the development cycle. This efficiency results in faster time-to-market for new applications, giving companies a competitive advantage.
Another significant use case involves data analysis. Organizations process vast amounts of data that demand intensive computing resources. IaaS allows businesses access to powerful computing capabilities, enabling them to perform complex analyses & derive valuable insights while managing costs efficiently.
Your Path to Effective IaaS Implementation
Transitioning to IaaS demands careful planning & execution. Organizations must start by defining clear objectives: what they hope to achieve through IaaS adoption. This foundational understanding informs decisions throughout deployment & ongoing management. Examination of current infrastructure can identify areas where IaaS can deliver maximum impact.
Next, organizations should evaluate potential providers based on factors such as pricing, features, scalability, & customer support. Engaging with multiple providers ensures businesses select a solution tailored to their unique needs. And another thing, companies must train employees on new tools & technologies, fostering a smooth transition.
Monitoring resource usage regularly assists in optimizing costs & ensuring performance meets expectations. Companies must also revise strategies as business needs evolve, remaining adaptive to both internal & external changes. Through consistent evaluation, organizations can maximize IaaS benefits, aligning their infrastructure with overall operational goals.
Implementing Security Best Practices in IaaS
Security always stands at forefront of concern for organizations adopting IaaS. Providers maintain extensive security measures; Be that as it may, customers must also take proactive steps to ensure data protection. One essential practice involves data encryption. By encrypting sensitive information both during transmission & at rest, businesses mitigate risks associated with data breaches.
And another thing, implementing strong identity & access management policies helps control who can access systems & data. Organizations must assign roles carefully, using the principle of least privilege to limit access only to individuals who require it. Regular audits & assessments of access controls help maintain a secure environment.
Lastly, organizations should adopt multi-factor authentication across their cloud environments. This extra layer of security significantly reduces chances of unauthorized access, protecting valuable data & resources from potential attacks.
Future Trends in IaaS
As technology evolves, so does landscape of IaaS. Organizations can anticipate several future trends shaping cloud infrastructure services. One prominent development involves increased adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) & machine learning (ML) applications. IaaS providers will likely integrate AI-driven solutions, enhancing automation & analytics efforts.
An expansion of edge computing also emerges as a significant trend. As businesses increasingly require low latency & high processing power, IaaS solutions will evolve, enabling computing performed at edge locations closer to data sources rather than centralized servers. This shift will yield improved performance for a variety of applications.
Lastly, sustainability concerns drive demand for greener IaaS solutions. Companies will seek providers committed to minimizing environmental impact, such as those utilizing renewable energy sources or optimizing resource usage. The trend toward greener practices illustrates growing awareness & responsibility toward maintaining environmental health.
Publisher: litslink.com
| Specification | AWS EC2 | Microsoft Azure | Google Cloud Platform | IBM Cloud | DigitalOcean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provider Name | AWS (Amazon Web Services) | Microsoft Azure | Google Cloud Platform | IBM Cloud | DigitalOcean |
| Year Launched | 2006 | 2010 | 2008 | 2017 | 2011 |
| Compute Options | EC2 Instances | Virtual Machines | Compute Engine | Virtual Servers | Droplets |
| Storage Solutions | S3, EBS, Glacier | Blob Storage, Disk Storage | Cloud Storage, Persistent Disk | Cloud Object Storage, Block Storage | Spaces, Volumes |
| Pricing Model | Pay-as-you-go | Pay-as-you-go | Pay-as-you-go | Pay-as-you-go | Flat rate, hourly |
| Global Availability | 24 regions | 60+ regions | 30+ regions | 19 data centers | 12 data centers |
| Scalability | Auto Scaling | Virtual Machine Scale Sets | Autoscaler | Auto-Scaling Groups | Flexible Scaling |
| API Access | Extensive APIs | Azure SDKs | Cloud Client Libraries | IBM Cloud APIs | API access available |
| Load Balancing | Elastic Load Balancing | Azure Load Balancer | Cloud Load Balancing | IBM Cloud Load Balancer | Load Balancers |
| Networking Features | VPC, Direct Connect | Virtual Networks, ExpressRoute | VPC, Cloud Interconnect | VPC, Direct Link | VPC, Private Networking |
| Security Features | Identity & Access Management | Azure Active Directory | Cloud Identity | IBM Cloud Identity | Cloud Firewalls |
| Compliance Standards | ISO 27001, HIPAA, PCI DSS | ISO 27001, HIPAA, PCI DSS | ISO 27001, GDPR, HIPAA | ISO 27001, HIPAA, PCI DSS | ISO 27001, GDPR |
| Container Support | ECS, EKS | Aks | Kubernetes Engine | IBM Kubernetes Service | App Platform |
| Developer Tools | AWS Toolkit | Visual Studio Integration | Cloud SDK | IBM Cloud CLI | Developer Hub |
| Support Plan | Basic, Developer, Business, Enterprise | Basic, Developer, Standard, Professional Direct | Free tier, Pay as you go | Lite, Standard, Premium | Basic, Pro, Business |
| Free Tier | 12-month free tier | 12-month free tier + $200 credit | Always free + $300 credit | Lite account available | Free trial with credit |
| Backup Options | S3 Backups, EBS Snapshots | Azure Backup | Cloud Storage Backups | Backup & Restore | Snapshots & Backups |
| Monitoring Tools | Amazon CloudWatch | Azure Monitor | Stackdriver Monitoring | IBM Cloud Monitoring | Monitoring Dashboard |
| Community & Documentation | Extensive Documentation & Community | Vibrant Developer Community | Rich Documentation | Good Documentation & Support | Active Community Forums |
What is an example of IaaS in the cloud computing space?
An example of IaaS is Amazon Web Services (AWS) Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2). It allows users to rent virtual servers on demand, providing scalable compute capacity.
How does IaaS differ from traditional hosting?
IaaS differs from traditional hosting by offering more flexibility & scalability. Users can adjust resources as needed, paying only for what they use, unlike fixed plans in traditional hosting.
Can you name another example of IaaS?
Microsoft Azure is another prominent example of IaaS, offering virtual machines, networking, & storage solutions that can be easily managed through their cloud portal.
What benefits does IaaS provide to businesses?
IaaS provides numerous benefits including cost savings, as businesses only pay for the resources they need, improved uptime with scalability, & reduced management overhead since infrastructure is managed by the service provider.
How is storage handled in an IaaS model?
In an IaaS model, storage is typically handled through scalable cloud-based solutions such as Amazon S3 or Azure Blob Storage, allowing users to store & retrieve data easily as per their requirements.
What industries commonly use IaaS?
Various industries such as IT, healthcare, finance, & e-commerce commonly use IaaS for its flexibility, cost efficiency, & ability to scale resources on demand.
What security measures are in place for IaaS services?
IaaS services typically incorporate a range of security measures, including data encryption, firewalls, & identity management systems, to help protect client data in their virtual environments.
Is it possible to host a website using IaaS?
Yes, it is entirely possible to host a website using IaaS. Users can set up virtual servers & configure them to run web applications, ensuring high availability & scalability.
What role does virtualization play in IaaS?
Virtualization is a cornerstone of IaaS, allowing multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server. This maximizes resource utilization & provides flexibility in managing workloads.
Can IaaS support big data applications?
Absolutely, IaaS can effectively support big data applications by providing scalable infrastructure & storage options necessary for processing & analyzing large datasets.
Conclusion
In summary, an example of IaaS is cloud services like Amazon Web Services or Microsoft Azure. These platforms offer the basic building blocks for your IT needs, allowing you to rent resources like servers & storage. This flexibility makes it easier for businesses to scale up or down based on their needs. By using Infrastructure as a Service, companies can save costs & focus on their core work instead of worrying about hardware. Overall, IaaS simplifies technology, making it accessible to everyone, from small startups to large enterprises, empowering them to grow without limits.


