A prime example of SaaS is Google Workspace, which provides a suite of productivity tools like Google Docs, Sheets, & Gmail accessible via the cloud. Businesses leverage Google Workspace for real-time collaboration, enabling teams to work simultaneously on documents & spreadsheets from anywhere. It’s widely used in remote work settings, education, & project management, enhancing efficiency & communication without the need for extensive IT infrastructure. Other notable SaaS examples include Salesforce for customer relationship management & Slack for team communication, illustrating the versatility & benefit of SaaS solutions across various industries.
What Is a Real World Example of SaaS? Explained with Use Cases. Discover what a real world example of SaaS is! Explore easy-to-understand use cases that show how SaaS helps businesses grow & succeed.

What is SaaS | Software as a Service Explained in 3-minutes | Cloud Computing | Intellipaat
What Is a Real World Example of SaaS? Explained with Use Cases What is SaaS | Software as a Service Explained in 3-minutes | Cloud Computing | Intellipaat What Is a Real World Example of SaaS? Explained with Use Cases
Understanding SaaS: A Deeper Insight
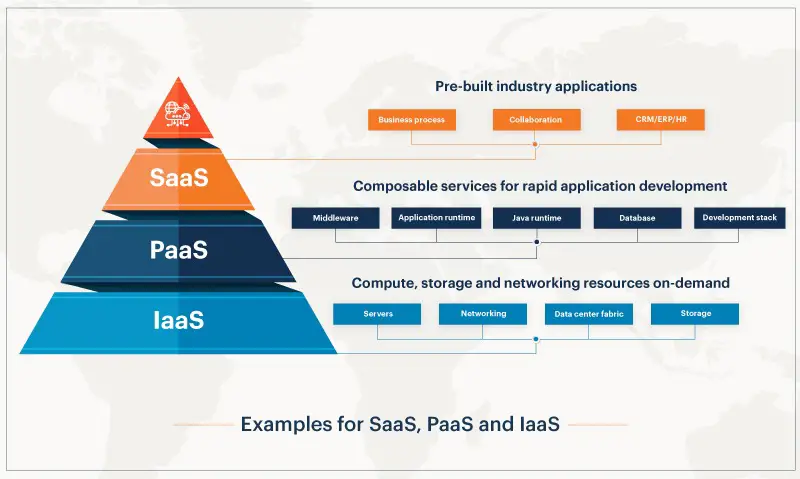
Software as a Service, often referred to as SaaS, represents a model where software applications are delivered over the internet to users. Instead of purchasing & installing software, users access applications through a web browser. This model eliminates issues related to updates, compatibility, & server management, making it a popular choice among businesses & individuals alike.
Characteristics of SaaS Solutions
Multiple key characteristics define SaaS solutions, making them highly attractive options. First, a subscription-based payment model allows users to pay based on usage or timeframes. This model provides flexibility, appealing especially to startups & smaller businesses. Second, with applications hosted in cloud environments, deployment occurs quickly, avoiding lengthy installations. Third, automatic updates ensure users always access latest features without manual intervention.
Benefits of Employing SaaS Applications
Adopting SaaS applications offers numerous advantages. Cost-effectiveness stands out as a major benefit; businesses save on hardware, maintenance, & IT support expenses. And another thing, remote access to applications enhances productivity, enabling teams to collaborate in real-time from various locations. Security concerns often arise, yet leading SaaS providers invest substantially in security measures, offering robust solutions that surpass typical on-premise systems.
Real World Examples of SaaS
Numerous examples illustrate how SaaS operates in real-world scenarios. From customer relationship management (CRM) platforms like Salesforce, which streamline sales processes, to project management tools such as Trello & Asana, which aid in task management. Each example showcases a unique aspect of how businesses utilize cloud-based software for enhanced efficiency.
Case Study: Salesforce
Salesforce stands as a prime example of SaaS. This CRM platform enables organizations to manage customer relationships effectively. With functionalities that cover marketing automation, sales forecasting, & customer service, Salesforce empowers businesses to enhance operational efficiency. Its cloud-based nature means businesses can easily scale operations without worrying about server limitations.
Key Features of Salesforce
- Integrated marketing automation tools
- Advanced analytics & reporting
- Customization options for specific business needs
- Mobile accessibility for on-the-go management
- Third-party application integrations
Case Study: Slack
Another exemplary SaaS offering comes from Slack. An application designed for team communication, Slack centralizes messaging, file sharing, & integrations with other tools. This platform enhances collaboration significantly, allowing teams from various locations to maintain connectivity. Organizations leveraging Slack benefit from increased productivity & streamlined communication channels.
Features of Slack
- Real-time messaging capabilities
- Channel organization for various topics
- Seamless file sharing & document collaboration
- Integration with other productivity tools
- Searchable history for easy reference
Case Study: Zoom
Zoom, known for video conferencing services, exemplifies another successful SaaS venture. With functionalities like webinars, virtual meetings, & conference calls, Zoom facilitates communication in remote environments effectively. Its intuitive interface welcomes users, from small businesses to large enterprises, making virtual meetups hassle-free.
Zoom’s Standout Features
- High-definition video quality
- Screen sharing options
- Virtual backgrounds for professionalism
- Recording capabilities for future reference
- Breakout rooms for group discussions
Practical Use Cases of SaaS in Different Industries
SaaS applications cater to multiple industries, each benefiting distinctly. Healthcare entities utilize SaaS solutions for patient management, enabling easy appointment scheduling & communication. Educational institutions leverage these tools to conduct online classes, ensuring seamless learning experiences during disruptions. Retailers benefit from SaaS by employing inventory management systems, optimizing stock levels, & improving sales tracking.
SaaS in Healthcare
Within healthcare, providers employ SaaS solutions for electronic health record (EHR) systems. These platforms enable doctors & nurses to access patient records securely, ensuring data remains update. And another thing, telemedicine services have gained traction; patients can consult with healthcare professionals remotely, enhancing access to care.
SaaS in Education
Educational institutions witness a growing trend of online learning platforms powered by SaaS. Solutions like Google Classroom create an environment for collaborative learning, facilitating assignment submissions & feedback through one centralized hub. Such models allow educators to reach wider audiences while providing personalized learning experiences to students.
SaaS in Retail
Retailers increasingly turn towards SaaS applications for inventory management. Solutions assist businesses in monitoring stock levels, facilitating automated reordering processes, & providing insights into sales trends. As a result, retail firms enhance operational efficiency while improving customer experiences through timely stock availability.
Examining Pricing Models of SaaS
The pricing structure for SaaS offerings varies based on features, number of users, & subscription length. Common models include monthly subscriptions, annual plans, or usage-based fees. Understanding such models aids businesses in selecting services that align with budgets & specific needs.
Common Pricing Strategies
| Pricing Model | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly Subscription | Pay a fixed monthly fee | Spotify, Netflix |
| Annual Subscription | Pay once per year, usually at a discounted rate | Microsoft Office 365 |
| Usage-Based Pricing | Pay based on actual usage | Amazon Web Services |
Challenges Faced by SaaS Providers
Despite numerous benefits, SaaS providers encounter several challenges. Data security remains a critical concern; as applications store sensitive information on remote servers, potential breaches could lead to significant issues. Customer churn presents another challenge; businesses need strategies to retain existing customers amidst competition from numerous alternatives. Ensuring seamless user experiences also poses difficulties, particularly when addressing issues like downtime or service outages.
Addressing Data Security Risks
Providers must prioritize security measures, investing in encryption, access control, & multi-factor authentication. Regular audits & compliance with regulations become essential components of a secure SaaS solution. By effectively managing these security risks, providers build user trust, circumventing potential legal ramifications resulting from data breaches.
Strategies for Enhancing Customer Retention
Improving customer retention requires deploying personalized outreach strategies, improved customer service, & continuous feature enhancements. By understanding user needs through feedback, providers can tailor offerings, ensuring services remain relevant & beneficial. Incentives such as loyalty programs may encourage continued subscription.
Future Trends in SaaS
Observing future trends in SaaS provides insights into where industry dynamics are headed. Artificial intelligence (AI) integration within SaaS solutions stands out as a prominent trend, enabling automation of complex tasks & providing personalized user experiences. And don’t forget, hybrid deployment models are gaining traction, allowing organizations flexibility between on-premise & cloud systems. The rise of vertical SaaS, focusing on industry-specific needs, may also redefine how applications evolve.
AI & Automation in SaaS
AI integration enhances productivity while simplifying customer interactions. For example, chatbots built into SaaS systems can manage queries, reducing workloads for customer support teams. And another thing, predictive analytics can improve business efficiency by anticipating user behavior & preferences, enabling proactive service adjustments.
Adoption of Hybrid Models
Organizations increasingly adopt hybrid models, combining advantages of both cloud-based & on-premise solutions. This flexibility allows businesses to control sensitive data locally while utilizing SaaS for other operational needs. As companies embrace hybrid models, service providers will likely experience heightened demand for customizable solutions that cater to unique needs.
Summary of Key Use Cases
Exploring various use cases clarifies how businesses effectively implement SaaS. Organizations worldwide leverage tools for multiple applications, enhancing efficiency, collaboration, & data management.
Notable SaaS Use Cases in Business
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Human Resource Management | Streamlined workforce management |
| Customer Support | Automated ticketing & chat support |
| Accounting Software | Real-time financial tracking & reporting |
In my experience, using a SaaS platform like Asana for project management transformed our workflow. With its intuitive interface & seamless collaboration features, we managed tasks more efficiently. Our team enjoyed the clarity brought by assigning deadlines & responsibilities, optimizing productivity significantly. This real-world application showcases how SaaS enhances daily operations.
Exploring Emerging SaaS Solutions
Continuous innovation within SaaS brings new applications to light. Startups are emerging with unique SaaS ideas, addressing niche requirements across various industries. As competition escalates, existing providers must remain vigilant about trends & user feedback, adapting their offerings continuously to stay relevant.
HealthTech Innovations
HealthTech companies are developing cutting-edge SaaS solutions targeting specific aspects of patient care. From telemedicine platforms that support remote consultations to chronic disease management apps, these innovations simplify healthcare delivery & improve patient outcomes. Such advancements showcase how SaaS continues shaping critical industries.
Finance & FinTech Developments
Finance sectors are witnessing rapid SaaS innovations, particularly within FinTech. These solutions enhance everything from personal finance management to investment tracking. By streamlining financial tasks, businesses can provide users with enhanced understanding & control over their financial affairs. As SaaS continues evolving, its impact on the finance industry becomes increasingly significant.

| Feature/Specification | Example 1: Salesforce (CRM SaaS) | Example 2: Slack (Communication SaaS) | Example 3: Shopify (E-commerce SaaS) | Example 4: Zoom (Video Conferencing SaaS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deployment Mode | Cloud-based | Cloud-based | Cloud-based | Cloud-based |
| Target Audience | Businesses of all sizes | Teams & organizations | Online retailers | Individuals & businesses |
| Primary Function | Customer Relationship Management | Team communication | E-commerce platform | Video conferencing |
| Pricing Model | Subscription-based | Freemium & subscription | Subscription-based | Freemium & subscription |
| Accessibility | Web & mobile apps | Web & mobile apps | Web & mobile apps | Web & mobile apps |
| Customization | High | Moderate | High | Low |
| Integrations | Extensive APIs & third-party apps | Numerous integrations | Many third-party tools | Various integrations |
| Onboarding Process | Guided setup & training | Simple & intuitive | Guided setup with tutorials | User-friendly onboarding |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Scalable for teams | Scalable for businesses | Highly scalable |
| Support Availability | 24/7 support | Standard business hours | 24/7 support | 24/7 support |
| Security Features | Data encryption & compliance | Data encryption | Secure payment processing | Encrypted communications |
| Mobile Compatibility | Full-featured mobile app | Full-featured mobile app | Full-featured mobile app | Full-featured mobile app |
| Analytics & Reporting | Robust reporting tools | Basic analytics | Comprehensive analytics | Basic meeting insights |
| User Management | Advanced user roles & permissions | Basic user management | Advanced user management | Basic user roles |
| Collaboration Features | Collaboration tools | Real-time messaging & channels | Multi-channel sales | Screen sharing & breakout rooms |
| Deployment Time | Quick setup | Instant activation | Quick setup | Instant activation |
| Trial Period | Free trial available | Free basic version | Free trial available | Free basic version |
| Customer Reviews | High satisfaction ratings | Positive feedback | High satisfaction ratings | Good user reviews |
| Content Management | Integrates with content tools | Basic file sharing | Product management features | Basic file sharing |
What is a real-world example of SaaS?
One of the most common examples of SaaS is Google Workspace, formerly known as G Suite. This platform offers various tools including Gmail, Google Drive, & Google Docs that allow users to collaborate & share documents effortlessly online.
How does SaaS benefit businesses?
SaaS provides businesses with scalability & flexibility. For instance, platforms like Salesforce allow companies to expand their customer relationship management capabilities without the need for significant investments in hardware or software.
Can you provide a specific use case for SaaS?
Consider a small business using Zoom for video conferencing. This SaaS solution allows them to connect with clients & team members remotely, reducing travel costs & improving productivity.
What challenges might users face with SaaS solutions?
While SaaS solutions offer many benefits, users may face challenges such as data security & loss of control over their data. For example, using Dropbox for file storage requires trust in the provider’s ability to keep data secure.
How does SaaS support remote work?
SaaS applications like Asana enable teams to manage projects & tasks from anywhere, facilitating remote collaboration & ensuring everyone stays on the same page.
Are there any industry-specific SaaS examples?
Yes, there are industry-specific solutions such as Shopify for e-commerce businesses, providing tools for managing online stores & payments, illustrating how SaaS can cater to unique business needs.
What is the pricing model for SaaS applications?
SaaS applications typically use a subscription-based pricing model, allowing users to pay monthly or annually, as seen with services like Adobe Creative Cloud which offers various plans based on user needs.
How does SaaS differ from traditional software?
Unlike traditional software that requires installation on local devices, SaaS applications are accessed via the internet, allowing for easier updates & maintenance, as exemplified by Microsoft 365.
Can SaaS integrate with other applications?
Many SaaS platforms, such as Zapier, offer integration capabilities that allow businesses to connect different applications to streamline their workflows, enhancing efficiency across various tools.
What is the role of SaaS in customer service?
Customer service platforms like Zendesk are excellent examples of SaaS solutions that help businesses manage customer inquiries & support tickets, improving customer satisfaction & response times.
How can SaaS enhance data analytics?
Tools like Tableau use SaaS models to provide businesses with powerful data visualization & analytics capabilities, enabling them to make data-driven decisions quickly & effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, SaaS is a game-changer in how businesses operate. By looking at real-world examples, like Google Workspace & Netflix, we see how software-as-a-service makes everyday tasks easier & more convenient. Companies can save time & money while improving collaboration & productivity. As well as, with SaaS, users don’t have to worry about updates & maintenance, as it’s all managed by the provider. Whether you’re a small startup or a large organization, embracing SaaS can transform your workflow & help you stay competitive in today’s fast-paced digital world.